
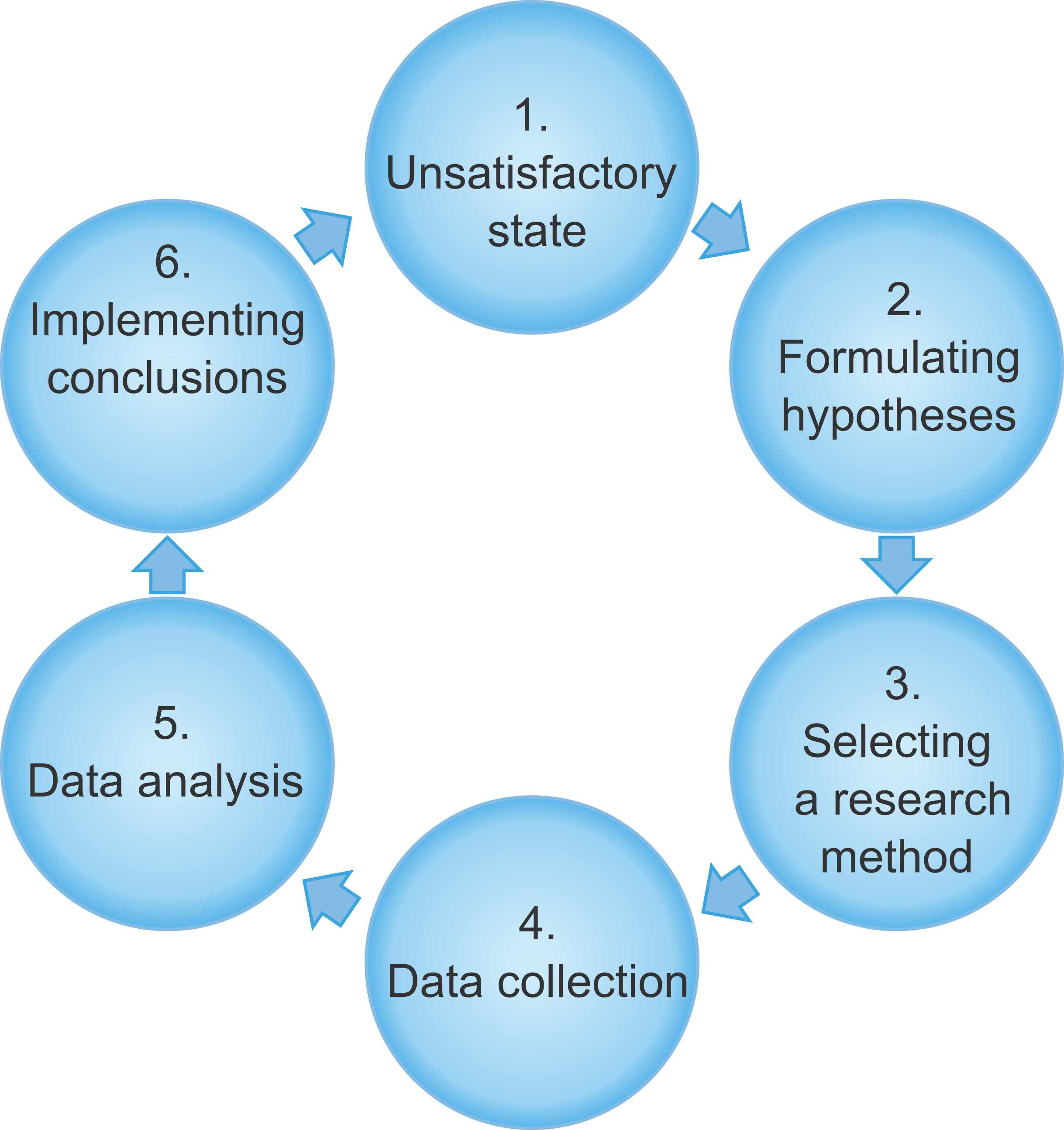
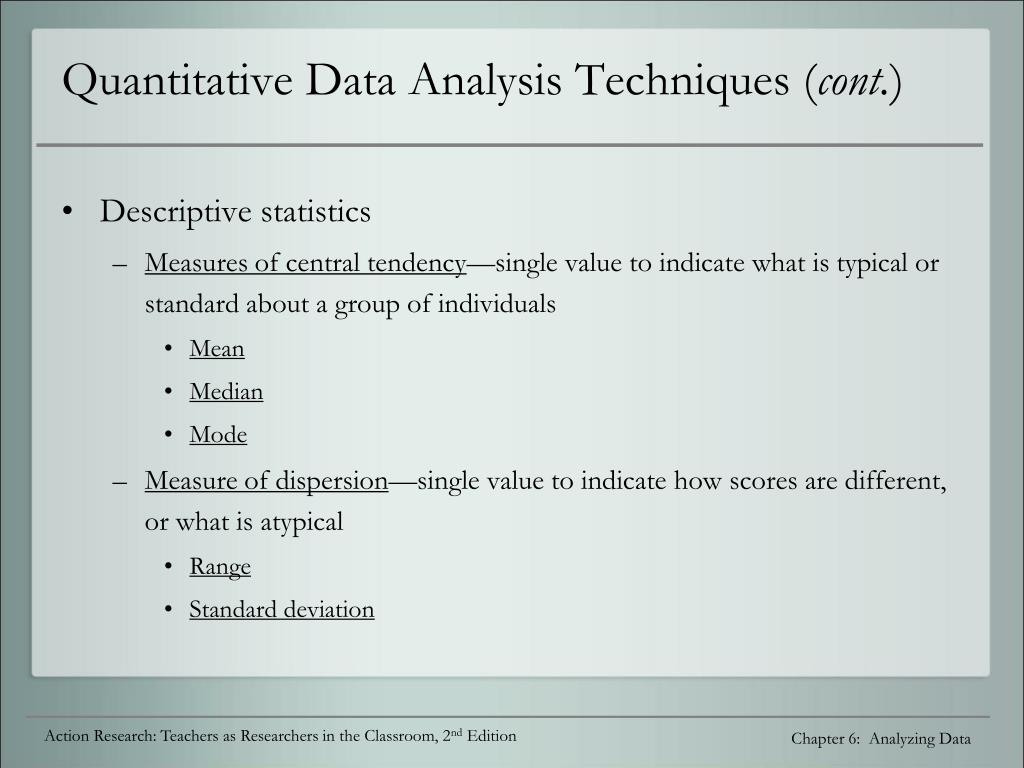
Which data analysis method you choose will depend greatly on the dataset you are dealing with and what you intend to achieve with it. If one proposes an explanation that seems probable, further data collection and analysis can always be conducted. In business, grounded theory is valuable where quantitative data is not available. Once again, statistical methods are left aside, and an individual must review the dataset to assess what they think might explain certain findings, using inductive reasoning. Grounded theory is a data analysis method that involves creating an explanation for a pattern or event. How they interpret the letter might be different to how another person would interpret the letter, but some analysis is still possible. Instead, the content must be analyzed by an individual, who will provide a subjective opinion on its meaning, tone, or other characteristics.Īs an example of content analysis, consider a person reading a letter. Since content is mostly qualitative data, statistical methods are less appropriate. Content analysisĬontent analysis is the broad name given to the process of analyzing the content. Qualitative Data Analysis MethodsĪlthough they are much less common, there are some techniques that can be used for qualitative data analysis. This is also a very popular method in the real world, especially in academia, since it’s essential to assess whether or not correlations are random. Usually, it’s used to confirm the relationship between two variables, to a certain level of confidence. Hypothesis testing is any statistical method used to confirm a hypothesis. It paints a picture of how much data can vary within a dataset. The range is the gap between the lowest and highest number in a dataset. In particular, using averages allows you to smooth out datasets and draw more accurate conclusions without averages, you might find yourself comparing data to an unusually low or high number. Regardless of which type of average you use, there’s a lot to be gained from knowing what the central value is in a dataset. The mode is the most frequently occurring number in the list. The median is the middle number in the list. It’s calculated by summing up the values in a dataset, and dividing the result by the number of values. The mean is what most people think of when you say the word average. In fact, there are three well-established types of average: the mean, median, and mode. We’re all familiar with the average - the central value in a set of data. As mentioned previously, many of these methods originate in statistics. Undergraduate students are not permitted in this class Instructor Consent:Ĭonsent required for all students Consent Note:Īll students must receive consent to register.Since quantitative data is ideal for analysis, let’s start by focusing on some of the many quantitative data analysis methods.
Identify the appropriate analytical tools for financial, market, quality, operational, and utilization analysis, and evaluate the analytic methods used by other students and provide feedback for improvement.Define the various data needs within healthcare and how data impacts decision making and accountability.


Auditors Allowed: No Undergrads Allowed: No Grading Restriction: Letter Grade or Pass/Fail Course Instructors:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
